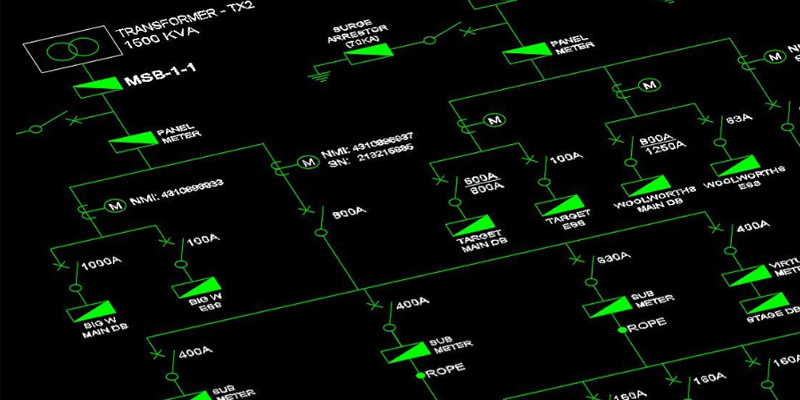
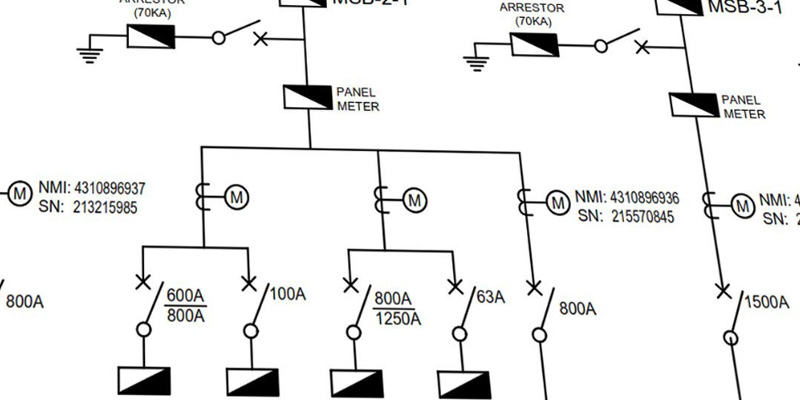
The Ultimate Guide to Drawing Single Line Diagrams (SLDs)
As Built Drawings Service Blog Hub | December 4, 2024
What is a Single Line Diagram (SLD)?
A Single Line Diagram (SLD) is a simplified representation of an electrical system, using standard symbols to represent components such as circuit breakers, transformers, busbars and cables. Unlike detailed schematics, SLDs display the electrical connections and power flow with a single line, making them easy to read and interpret.
Why Are Single Line Diagrams Important?
- Simplified Visualisation
- SLDs reduce complexity by consolidating multiple lines and phases into one.
- Efficient Communication
- They serve as a map for electrical engineers, contractors and inspectors.
- System Planning and Design
- SLDs are used during and after the design phase to ensure proper system functionality and capacity.
- Operation & Maintenance
- They help teams quickly troubleshoot issues and plan upgrades.
- Regulatory Compliance
- SLDs are often required for permits, audits and safety assessments.
Steps To Create a Single Line Diagram
- Understand the System Requirements
- Identify all components involved: power sources, transformers, switchgear etc.
- Clarify the voltage levels and distribution hierarchy.
- Arrange Components Logically
- Position the main power source at the top or beginning of the diagram.
- Place loads and distribution points at the bottom.
- Draw transformers and switchgear between power sources and loads.
- Use Standard Symbols
- Ensure all elements and symbols follow electrical standards for consistency.
- Connect Components with Lines
- Draw straight lines to represent connections.
- Use arrows to indicate the direction of power flow.
- Label Everything Clearly
- Label components, voltage levels and equipment ratings.
- Include notes for additional clarity, such as relay settings or fuse sizes.
- Verify the Diagram for Accuracy
- Cross-check with system requirements and equipment specifications.
- Ensure the diagram reflects all safety protocols and redundancy needs.
- Keep It Clean and Simple
- Avoid clutter by focusing on essential elements.
- Include a Legend
- Provide a key to explain symbols used in the diagram.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Omitting Key Components
- Ensure all relevant equipment is represented.
- Using Incorrect Symbols
- Follow standard electrical symbols to avoid miscommunication.
- Neglecting Voltage Levels and Ratings
- Always label voltage and current capacities.
- Failing to Update the Diagram
- Keep the SLD current with system changes for safety and accuracy.
Conclusion
Drawing a precise Electrical Single Line Diagram is essential for the efficient design, operation and maintenance of electrical systems. A well drafted SLD simplifies complex systems, streamlines communication and ensures smooth project execution. By following best practices, using appropriate symbols and drafting standards, you can create SLDs that serve as invaluable guides throughout the lifecycle of any electrical project.
Need Help with Your SLD’s?
At Design Assist Partners, our team of experts is here to assist with drafting and updating your Single Line Diagrams. Refer to our FAQ’s for further information or contact us today to learn more about our tailored solutions for Electrical Single Line Diagrams.